Root Cause Analysis in ISO-Integrated Systems: Solving Problems, Not Just Hiding Them
Integration of management systems helps organizations reduce operational costs by eliminating duplicate activities, minimising downtime, and improving overall productivity. By integrating different management systems into a single system, organizations can reduce the maintenance effort required to make multiple systems operate effectively.
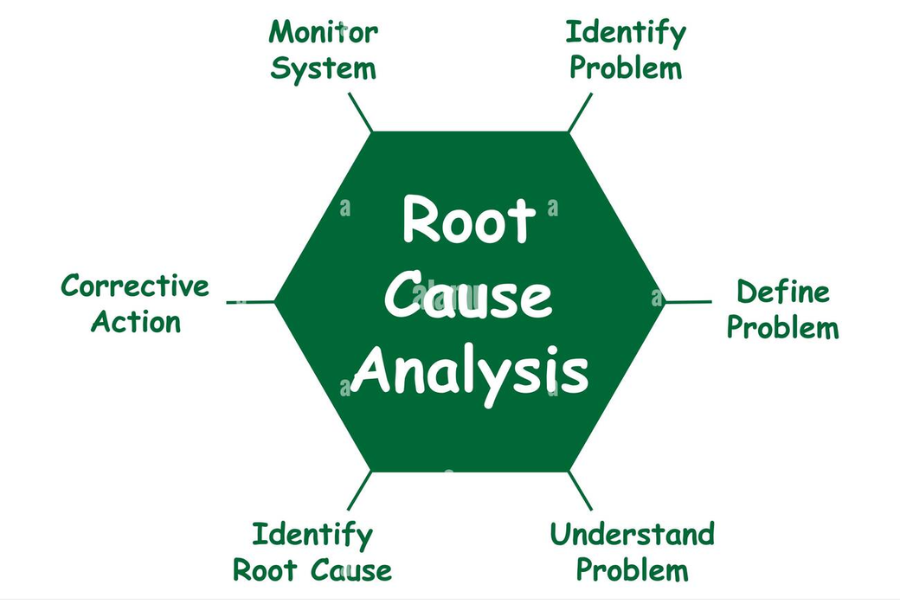
Why is Root Cause Analysis?
Root cause analysis is a problem-solving method that is used in identifying the root causes of problems or incidents. By identifying and correcting these root causes, we can prevent similar issues from occurring in the future. To perform a root cause analysis, start by defining the problem in specific terms. Review the data to determine which root causes are most likely. Also, it designs and implements solutions to rectify the root causes. RCA monitors the results to ensure the problem has been resolved. Through the utilization of root cause analysis, you can prevent issues from recurring and improve our processes for the future.
What are Integrated Management Systems?
An integrated management system (IMS) combines various management frameworks such as quality management, environmental management, and occupational health and safety management into a single, cohesive system. This integration enables organizations to streamline their processes, reduce duplication, and enhance overall efficiency.
What is ISO?
ISO stands for the International Organization for Standardization, a global body that develops and publishes standards for various sectors and industries. ISO standards provide instructions and best practices for quality, safety, efficiency, and reliability in products and services. They are meant to be used by any organization, large or small, in any industry. The series of standards designated as ISO 9000 focuses on quality management and quality assurance. The most recognized and utilized standard in this series is ISO 9001. It provides the requirements for creating, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving a QMS that meets customer and regulatory expectations. ISO 9001 is based on seven quality management principles, such as customer focus, leadership, involvement of people, process approach, improvement, decision-making based on evidence, and relationship management.
How to Integrate Root Cause Analysis with ISO?
Integrating RCA with ISO entails aligning your RCA process with the ISO 9001 principles and requirements. For this, you have to define your RCA process as part of QMS documentation, i.e., objectives, scope, roles, responsibilities, methods, tools, and outputs. The process shall be in line with your quality policy and objectives and cover all the relevant stages in the product life cycle. You have to implement your RCA process as part of quality operations. When there is a nonconformity, complaint, or product or service failure, use appropriate RCA techniques to identify the root causes.
Document findings and actions in a record or report, then notify appropriate stakeholders and customers. Additionally, you must quantify and monitor the effectiveness and efficiency of your RCA process via KPIs such as the number of RCAs conducted, time taken to conduct them, cost of RCAs, recurrence frequency of issues and customer satisfaction ratio. Collect and examine data from the process for trends, patterns and improvement areas. Finally, use data and feedback from RCAs to create and implement corrective actions that eliminate root causes of issues and prevent them from happening in the future. Reviewing the RCA process is also essential to ensure it meets the changing expectations of customers.
How to Conduct Root Cause Analysis?
While root cause analysis can be done by one person using most of the tools, its outcome is always better when a group of people get together to find the causes. The individuals who will ultimately be responsible for removing the discovered root causes must be a major part of the analysis team that ventures out to find them.
A typical structure for a root-cause analysis in a company may include the following elements-
- It is determined to form a small team to perform the root cause analysis.
- Team members are selected from the organizational business process/area where the problem exists.
- A line manager with decision-making authority to implement solutions.
- A quality improvement specialist in a scenario where the rest of the team lacks experience in this kind of work.
- The analysis lasts about two months. An equal amount of time during the analysis is spent on defining and understanding the problem, brainstorming its possible causes, cause and effect analysis, and devising a solution to the problem.
- Throughout the analysis period, the team meets at least once a week or two to three times a week. The sessions are always short, no more than two hours, and since they are meant to be creative sessions, there is a very fluid agenda.
- Once the solution has been developed and the decision to act has been reached, there can be a day to several months before the change is completed, depending on what is needed in the implementation process.
Who Should Be Involved In Root Cause Analysis?
First, security analysts and incident response team members are essential. These experts are on the front lines, detecting and responding to security incidents. They have the technical knowledge needed to analyze attack vectors, system vulnerabilities, and the timeline of events. Their insights are crucial for identifying the technical root causes, such as where malware entered or what configuration weaknesses were exploited.
Next, we have IT operations and system administrators. These individuals manage the infrastructure and systems that were affected by the incident. Their understanding of system configurations and network architecture helps clarify how the incident occurred from an operational standpoint. They can provide context that is vital for a thorough analysis.
Developers and application owners also play a significant role, especially if the incident involves software flaws or vulnerabilities. They can share details about recent code changes, deployments, and any known bugs that may have contributed to the incident. Their input is key to identifying root causes related to the software.
Management and governance representatives should not be overlooked. Their involvement ensures that organizational policies and compliance requirements are taken into account. They can help identify root causes related to policy gaps or insufficient oversight that may have allowed the incident to happen.
Human resources and training coordinators are important as well. Many incidents stem from human error or lack of training. These teams can provide context about staff capabilities and training programs. Their insights support identifying human and organizational root causes.
If the incident involves external services or supply chain components, third-party vendors or partners should also be included. Their participation is crucial for understanding their systems and controls, as well as how they handled the incident.
Lastly, legal and compliance teams must be involved to ensure the analysis adheres to regulatory requirements. They can address any legal implications that arise from the incident. By including these diverse stakeholders, organizations can gather comprehensive data and perspectives. This collaborative approach helps differentiate between superficial causes and true root causes.
Conclusion
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is most effective when backed by genuine care and commitment. To maximize its benefits, organizations should avoid common pitfalls such as rushing the process, attributing issues solely to human error, or proceeding without the support of management. The objective of RCA is not only to address current problems but also to prevent their recurrence in the future. With the right approach, RCA can lead to more effective ISO management systems, stronger teams, and improved operational efficiency.
Keep an eye for more latest news & updates on Ancient Artz!